- Heating, Air Conditioning, Electricity
- Heat pump, Ventilation, Air conditioner
- FRANKI FOUNDATIONS BELGIUM
- Products
- Catalogs
- News & Trends
- Exhibitions
Energy pile





Add to favorites
Compare this product
Description
The energy pile, also called "heat exchanger pile", is a pile equipped with individual or several pipe circuits in order to enable exchange of heat with the surrounding soil. The function of energy piles is dual. The first function consists of transferring load from a construction into the bearing layer. The secondary function is the use as heat exchanger with the soil. Energy piles are installed either using soil displacement techniques (see 'Construction sequence'), or soil excavation systems.
Construction sequence
The functioning of the installation takes place over an annual cycle.
In winter, with the aid of a heat pump, when the water is colder than the soil, heat is removed from the circulating fluid (and indirectly extracted from the soil) and renders a higher temperature to the heating.
In summer, conversely, when the water is warmer than the soil, heat is dissipated into the soil for cooling
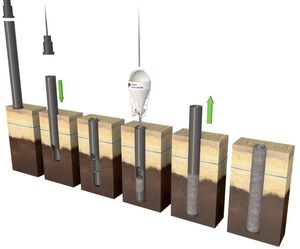
1., 2. & 3. During the screwing-in phase, a soil displacing screw head inserts the guide tube to the correct design depth
4. During the screwing-out phase - as the auger is simultaneously withdrawn while rotating - concrete is pumped into the borehole through the hollow central tube of the auger.
5. & 6. The reinforcement, fitted with integrated heat exchangers in HDPE (‘collector pipes’), is then placed into the concreted pile. A heat exchange fluid, usually simply clear water, circulates in an U-shaped pipe circuit (‘pipe loop’) located between the piles and a heat pump (HP) and is heated or cooled by the surrounding soil.
Other FRANKI FOUNDATIONS BELGIUM products
Pile foundations
*Prices are pre-tax. They exclude delivery charges and customs duties and do not include additional charges for installation or activation options. Prices are indicative only and may vary by country, with changes to the cost of raw materials and exchange rates.